
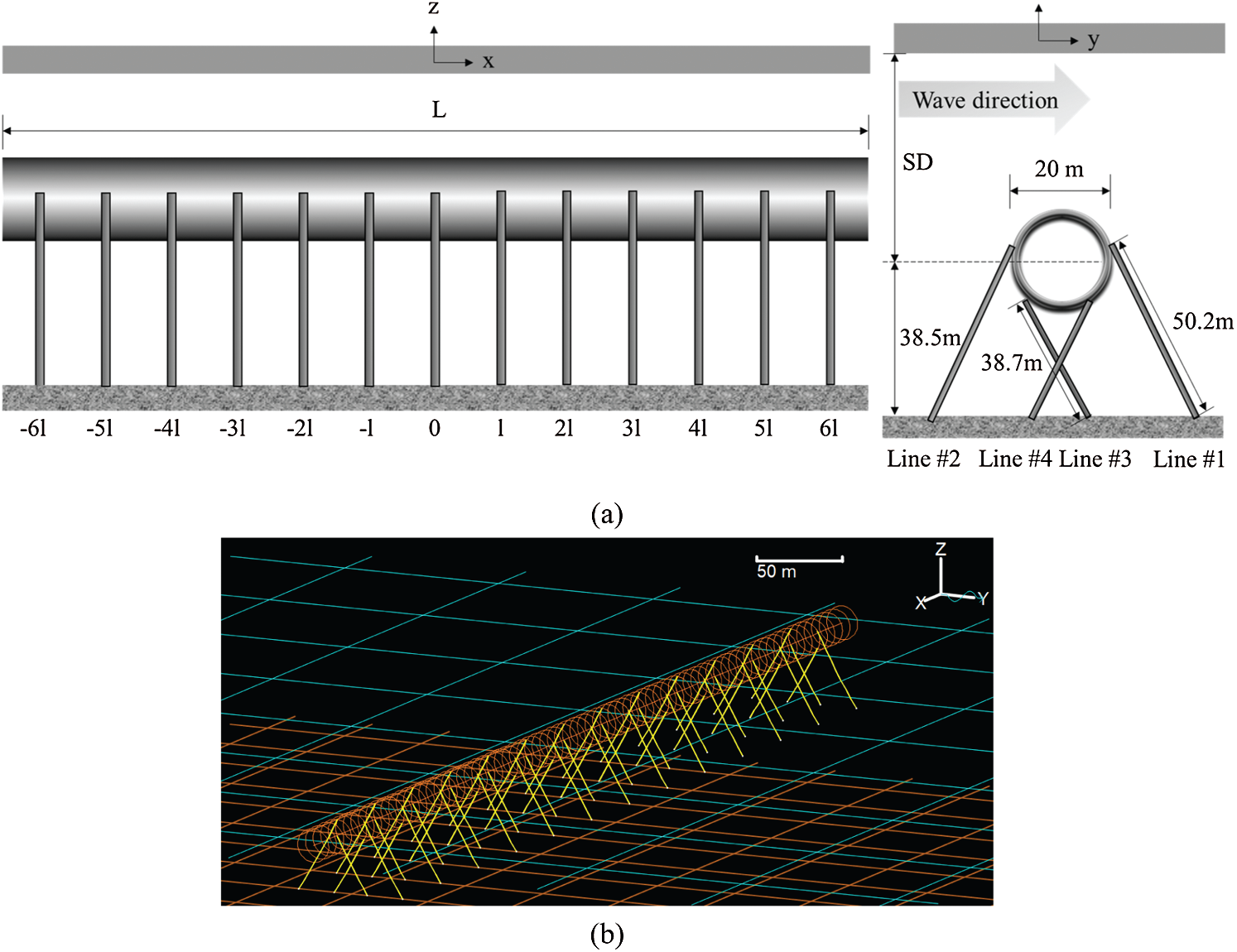
If a slam coefficient is zero then no slam force is applied for motion through the water surface in the corresponding direction. (Department of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Marine Engineering, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK) Abstract: This paper studies the behavior of a mooring system, in water depths from 300m to 3000m, using. Separate values are required for water entry and water exit, and each can be set either to a constant slam coefficient value or to be variable with submergence relative to the surface. Influence of Water Depth on the Hydrodynamics of Deep-water Mooring Characteristics. The slam force, as the line enters or exits the water, is determined by the slam force data. Inertia coefficients are not specified for homogeneous pipe, but are internally set to '~'.
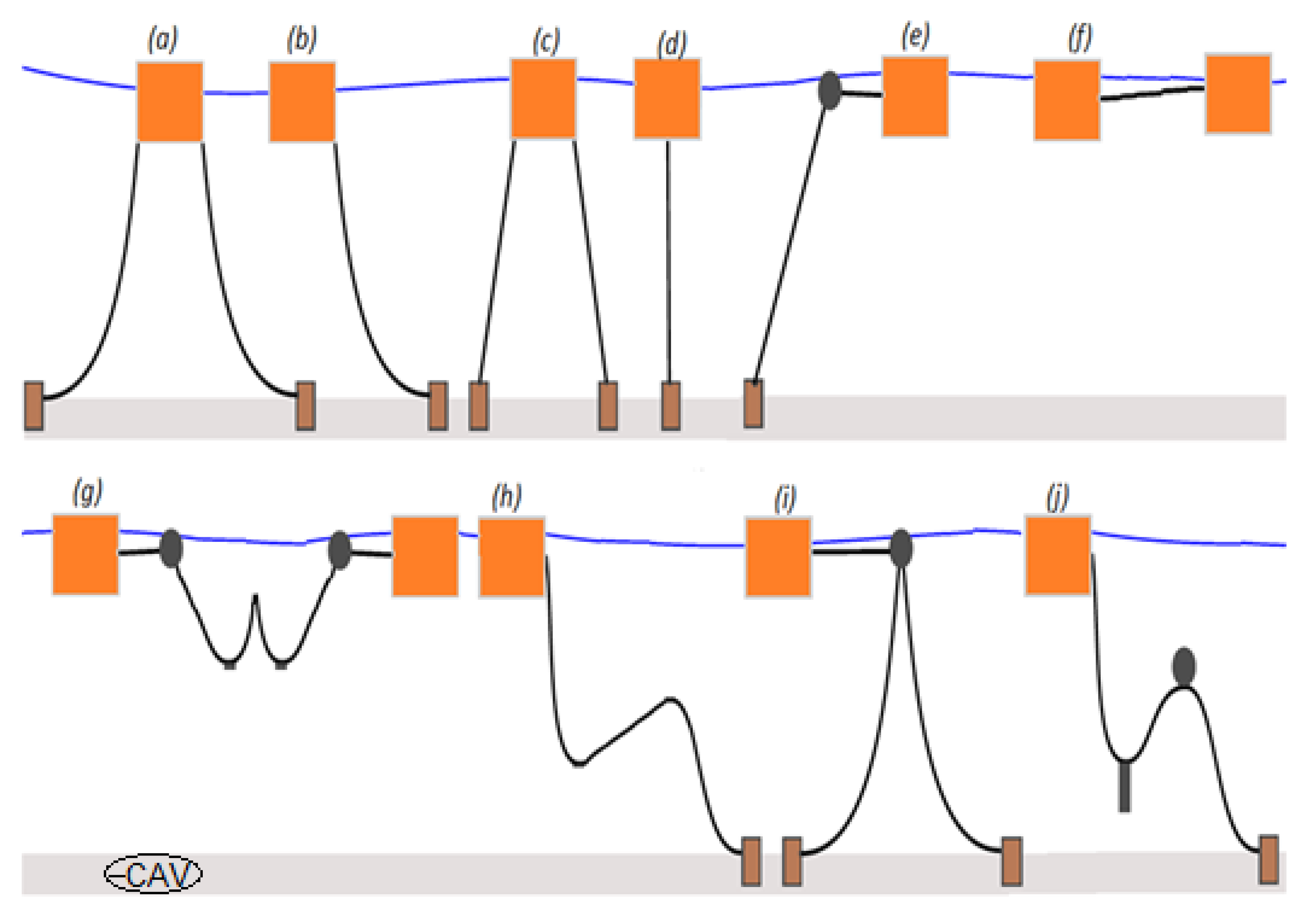
Orcaflex manual added mass coefficients of mooring chain plus#
A value of '~' here, however, is allowed for both $x$ and $y$ coefficients and tells OrcaFlex to use the usual 'Froude-Krylov plus added mass' formulation for inertia: for a constant added mass coefficient $\Ca$, this is equivalent to setting the coefficient $\Cm$ to $1\Ca$. The inertia coefficients $\Cm$ are defined in the same way as $\Ca$, for normal and axial directions, though only constant values are allowed. A value of '~' for the $y$ coefficient may be used, to mean 'same as the $x$ coefficient'. Added mass effects are calculated using the displaced mass as the reference mass for each cylinder (either the instantaneous or the fully-submerged displacement is used, depending on the form of the data – see the theory section for details). The variability may be defined either close to the sea surface or close to the seabed. The added mass coefficients $\Ca$ are defined for normal ($x$ and $y$-directions) and axial ($z$-direction) flow the $x$ and $y$ values may be, independently of each other, constant or variable, while the $z$ coefficient must be constant. Mooring component masses, cross sections, added mass, damping, and spring rates do not scale well using Froude similitude. Under the given moderately rough wave conditions and track irregularity, the moving train also meets the safety and passenger-comfort criteria at high (80 m/s) train speed.Line types: Added mass, inertia, slam data It is seen that the influences of moving trains on the dynamic responses of the SFT are small.
For more complex coupling of SFT dynamics with multi-car trains in random waves, the presently developed simulation program is applied. In the simple case of moving mass inside SFT in calm water, SFT's dynamic responses and mooring tensions agree well with those by a commercial program, OrcaFlex.

Accordingly, the train-tunnel coupled dynamics formulas are derived. The interaction between the tunnel and the train is taken into consideration based on the correspondence assumption and the simplified Kalker linear creep theory. The train is modeled by using the multi-rigid-body dynamic method, in which a train element is composed of seven constituent rigid sub-bodies. 7 5.13.3Spar Buoy and Towed Fish Added Mass and Damping198 5.13.4Spar Buoy and. Wave-induced hydrodynamic loads are estimated by the Morison equation for a moving object. w 1 OrcaFlex Manual Version 9.6a Orcina Ltd. The tunnel is coupled with mooring lines through a specially devised connection method with linear and rotational springs. The equations of motion for a tunnel and mooring lines are based on the FE (finite element) rod theory with the Galerkin formulations. Due to the unsteady pressure field generated by the incident wave.

Hydrodynamic loads in phase with the velocity of the body. In this study, a time-domain coupled hydroelastic dynamics model has been developed to solve the tunnel-mooring-train interaction under wave excitations. Hydrodynamic loads in phase with the acceleration of the body. A submerged floating tunnel (SFT) is considered as an effective alternative to conventional bridges and underground/immersed tunnels for passing through deep water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
